School Nurse: A Full Guide
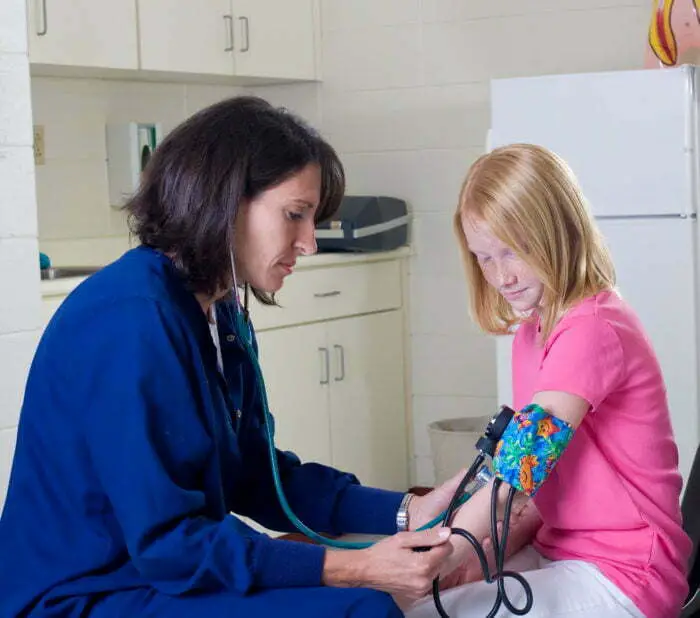
Every student's ability to learn and excel in school is heavily influenced by their well-being. A student whose mental or physical health is impaired cannot focus in class or retain what's taught. Unhealthy students are also more likely to miss school, which ultimately affects their learning. For these reasons, a school nurse is a vital aspect of education.
Well-trained school nurses can improve school health and enliven the school environment, which can subsequently improve community health. Furthermore, proper school nursing can also help students earn better grades, which encourages them to move on to further education and establish bright careers.
Often, school nurses are the only healthcare resource students have. A 2018 report by the U.S. Census Bureau revealed that over 4.3 million children in the country do not have health insurance. Additionally, a study by the NCBI reveals that the lack of access to medical care can deteriorate physical and emotional health, preventing children from achieving their full potential as adults.
School nurses provide students and staff with a wide array of health services, playing a pivotal role in the education system and overall school health.
A career in nursing can be appealing to many for many different reasons. However, if you have a strong desire to advocate for the good health of children in school, starting a career as a school nurse may be your calling.
In this comprehensive guide, we detail everything there is to know about school nursing and break down how you can become a school nurse.
What is a School Nurse?
A school nurse is responsible for assessing and treating students who experience illness or injury during the school day and also during after-school activities. School nurses must determine if a higher level of care is required and take the necessary steps to provide proper care to the student.
In the school environment, a nurse encounters different problems than they would in a hospital setting. Before deciding to become a school nurse, it is vital to understand that school nurses do not just deal with health-related issues in the school. School nurses must also offer health education, to both students and staff as required.
In simpler words, school nurses play leadership roles and are required to offer both: quality health services and health education. According to the National Association of School Nurses, the medical and educational roles school nurses play to promote positive behavioral health in students.
These nurses often work with counselors to ensure every student gets the care they need for their physical and mental health.
While providing school health services is a core responsibility of a certified school nurse, these health care professionals must also be aware of social and economic factors that can affect students. A school nurse may need to address several issues outside of the school's bounds that can cause harm to students individually and to the student population as a whole.
School nurses have a discernably large set of responsibilities that extend beyond fulfilling the health needs of the school community. Strong communication skills are a must-have since these healthcare providers must communicate with staff, parents, and other healthcare providers frequently.
History of School Nursing
Originally, the role of a nurse in a school setting was to check the student population was not disease-stricken. In the event that a student had a disease, the healthcare professional must determine if the disease is contagious and requires immediate treatment. These professionals were also responsible for ensuring that the student is isolated from other students.
As vaccines and antibiotics became widespread, the role of the school nurses changed drastically. Today's children face many different problems than students did 50 years ago. Currently, the education system requires skilled healthcare professionals that can work with students to manage school health problems such as:
- Chronic illnesses;
- Learning disabilities;
- Mental health issues;
- Behavioral problems; and
- Other common health problems.
Since school nurses focus on a specific patient population and are required to possess a unique skill set, school nursing is considered a specialty practice.
What Does a School Nurse Do?
School nurses perform the critical role of ensuring the good health of the school's students. Another important role is to ensure all school health services programs are implemented correctly.
The responsibilities of a school nurse include:
- Monitoring the glucose of students
- Assisting families with obtaining health insurance
- Stabilizing a student until emergency services arrive
- Administering medications (routinely or as required)
- Assessing mental health issues and providing proper support
- Providing wound care in case of injury
- Ensuring the school's infection control standards are met
- Performing CPR or other lifesaving procedures if warranted
- Contacting the student's parents or emergency services if required
- Educating and communicating with parents about contagious diseases and other health-related issues
- Maintaining health records
- Assisting families with obtaining healthcare outside of the school
- Carrying out the yearly vision, hearing, physical, and mental health screenings
- Ensuring all students are vaccinated according to the school district requirements
- Submitting students' vaccination-related documentation to the state
- Assisting with free or reduced lunch programs
- Providing health education to students and staff privately or in group settings
It is critical for school nurses to fulfill their several responsibilities since it directly influences student health and community health. All school districts have vaccination rules and school nurses must ensure every child is vaccinated and has valid documentation.
Schools often have limited healthcare resources compared to hospitals, and the school nurse must know when the student's parents or emergency services need to intervene.
Where Do School Nurses Work?
School nurses are registered nurses with relevant work experience and certifications that prepare them to take on all of the responsibilities that entail the role. School nurses may work in the following educational settings:
- Public/private elementary schools
- Middle schools
- High schools
- Department of education
- Vocational schools
- Juvenile correction facilities
- Alternative schools
- Hospitals
- Pre-schools
- Summer camps
- Overseas military bases
Colleges and universities also employ school nurses to ensure that students receive all the benefits of their health programs. Some school nurses find work in the local Department of Health and help manage school health on a much larger scale.
School Nurse Salary
A school nurse's salary can vary drastically from state to state. Sometimes, there are huge variations in salaries within the same state. If you're aspiring to become a school nurse, you must remember that work location will impact your pay significantly.
In some school districts, school nurses are paid in the same range that the teachers are paid. However, these nurses are typically Certified School Nurses. Registered Nurses, on the other hand, are typically paid an hourly rate. While schools may report salary data at a state level, the pay for these professionals is rarely uniform across a state.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that the average annual salary of Registered Nurses is $75,330. That said, the bureau does not report any specific data about the pay range of school nurses. Salary.com reports that the national average salary for these healthcare professionals is $51,868.
Besides the nurse's qualifications, the pay offered is also influenced by the cost of living in the area. If the cost of living is higher in the area, you can expect the pay to be higher when compared to cheaper areas.
You must bear in mind that unlike other roles in nursing, you will not be required to work overtime if you're a school nurse. Most schools offer a yearly salary and rarely have overtime mentioned in the contract. You will only make more money as you earn more experience and qualifications.
Job Outlook
The job outlook for registered nurses is high, with the BLS expecting a 7% job growth by 2029. Finding a job as a school nurse shouldn't be difficult as long as you get the right education.
Benefits
While the workplace setting may be different from the typical nurse, school nurses enjoy all of the benefits that every other nurse enjoys. You can expect:
- Family leave of absence
- Maternity leaves
- Retirement options
- Insurance (health, dental, and vision)
- Discounts on products
- Tuition and certification reimbursements
- Entry passes to nursing conferences
- CEU reimbursements
- Professional organization reimbursements
How Do I Become a School Nurse?
To get hired as a school nurse, you must first become a registered nurse and earn the right certification. While you can get hired as an RN right after you earn your RN license, you will need to study for a few more years before you earn the right qualifications to be eligible for well-paying school nurse positions.
Step #1: Get Your Bachelor's of Science in Nursing (BSN)
Before getting your RN license, your first step is to earn a BSN. Completing the course will give you a fundamental understanding of nursing. It takes four years to earn a BSN degree, and the course spans a wide range of concepts.
You will learn how to care for populations regardless of their age. You will gain insight into everything from pediatric to adult nursing care. It is not uncommon for student nurses to take up courses in psychiatry and gerontology.
To get the BSN degree, you will need to complete courses covering subjects such as:
- Anatomy;
- Microbiology;
- Public health;
- Nutrition;
- Pharmacology;
- Mental health; and
- Pathophysiology.
Besides learning these subjects, you will also learn all of the principles and theories of nursing. These will enable you to apply your knowledge correctly to patients from different backgrounds that are suffering from different health conditions.
Communication is one of the pillars of nursing, and your nursing program will teach you to effectively communicate with your colleagues in the workplace. Clear communication is a vital skill that will help you as a medical professional helping patients and staff to meet their healthcare goals.
Additionally, you will learn evidence-based skills through the real-world clinical training you receive in the nursing program. Firsthand experience will give you a look at the full scope of all that the profession involves.
Modern nursing programs also provide their students with computer science training. It ensures that the nurse can use a wide array of technological innovations to treat patients.
Step #2: Pass the NCLEX-RN Exam
After you graduate, you will need to sit for the National Council Licensure Exam (NCLEX-RN). It is a computerized test that every nursing graduate seeking licensure must take. The test is scored by the NCSBN, and you will only get your license if you pass the exam.
The exam comprises questions that test nurses on all of the training they have received in their nursing program. The test helps protect public health by ensuring every nursing candidate has the necessary skills to provide the highest quality of health services.
Before you take the est, you will need to apply for a nursing license to the nursing board in your state. If you meet the criteria, you will receive a confirmation of eligibility and can then take the exam.
You can apply for school nurse positions right after you earn your RN license. However, getting certified and earning an MSN can help you advance your career and earn a better salary.
Step #3: Meet the Certification Requirements
The next step in the process is to earn the certification of school nurses. To get become eligible for certification, you will first need to complete a minimum of 1000 hours of clinical experience. Alternatively, three years of full-time academic experience is required.
The NBCSN requires candidates to have experience since it helps students build the necessary experience before they work independently in an educational setting. To earn the experience, you may work in any hospital or doctor's office after passing the national exam.
Step #4: Pass the Certification Exam
After you earn your bachelor of science in nursing, pass the NCLEX, and earn the experience (if required), you can finally take the School Nurse Certification Exam. The exam is administered by the National Board for Certification of School Nurses and comprises 250 questions. The test is designed to ensure that you'll be able to work independently in a school setting.
You are given four hours to complete the test, and the questions in the test will measure your understanding of the health problems you may encounter in a school setting. You will also be tested on your knowledge of interventions that keep students in a school healthy. The work setting requires nurses to deal with unique ethical issues, and therefore, the exam includes questions related to this.
The exam's questions are compiled from a range of different topics, and hence the exam is always different. You will need to retake the exam every few years to keep your certification. How often you must retake the test changes from state to state. Additionally, you will need to complete a specific number of continuing education hours, and these requirements also vary by state.
Step #5: Meet State Level Requirements (If Any)
You must remember that school nurses are governed at the state level, and therefore, the requirements for becoming a school nurse are always identical for all nurses in the state.
That said, educational requirements change from state to state, and they often vary greatly. For instance, the state of Arizona requires you to obtain a school nurse certificate before you can work as a school nurse. In California, besides your bachelor's degree, you must earn 26 additional credits in school nursing to be eligible for a job.
Therefore, before you apply for any jobs in your state, make sure you fully investigate the requirements.
Sponsored Programs
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need continuing education credits after completing my degree to become a school nurse?
Some, but not all states have continuing education requirements. You will need to research your state's demands to ensure you keep your qualifications.
Do school nurses need to work in the summer?
Being a school nurse is very different from being a nurse in a hospital. There are no long and demanding hours — you will only need to work Monday through Friday. Furthermore, you will have the summer off.
Are all school nurse roles full-time?
You may work part-time or full-time depending on the school's requirements.
How do school nurses influence school health?
School nurses support the school health environment by providing quality healthcare to students and staff alike. These professionals are capable of addressing physical, mental, and social health needs. Providing every student with the right kind of support sets them up for success in the future.
What is the National Association of School Nurses?
The NASN or National Association of School Nurses is a leading organization that offers school nursing programs. The organization also provides peer-reviewed clinical journals to help school nurses advance their knowledge and improve their practice. Learn more about the national association of school nurses.
Should I Become A School Nurse?
Besides having physical health expertise, successful school nurses are also capable of helping students navigate mental health issues. These professionals have a deep understanding of school policy, laws, and are very comfortable with working with children.
Excellent communication skills are a must-have since you will need to communicate with teachers, students, and parents. You may also need to work to ensure a student's social well-being and take anti-bullying measures. It is important that you remain comfortable when resolving conflicts.
If you pick the right nursing program and work hard, you will learn everything you need to know to become successful at school nursing. It is a respected role, pay is great, and seeing children go home healthier can be gratifying. You can advance your career as a school nurse later down the road by getting certified or earning an MSN.

